Chargefox Reveals Engineering Challenges Of Its Australian Car Charging Network
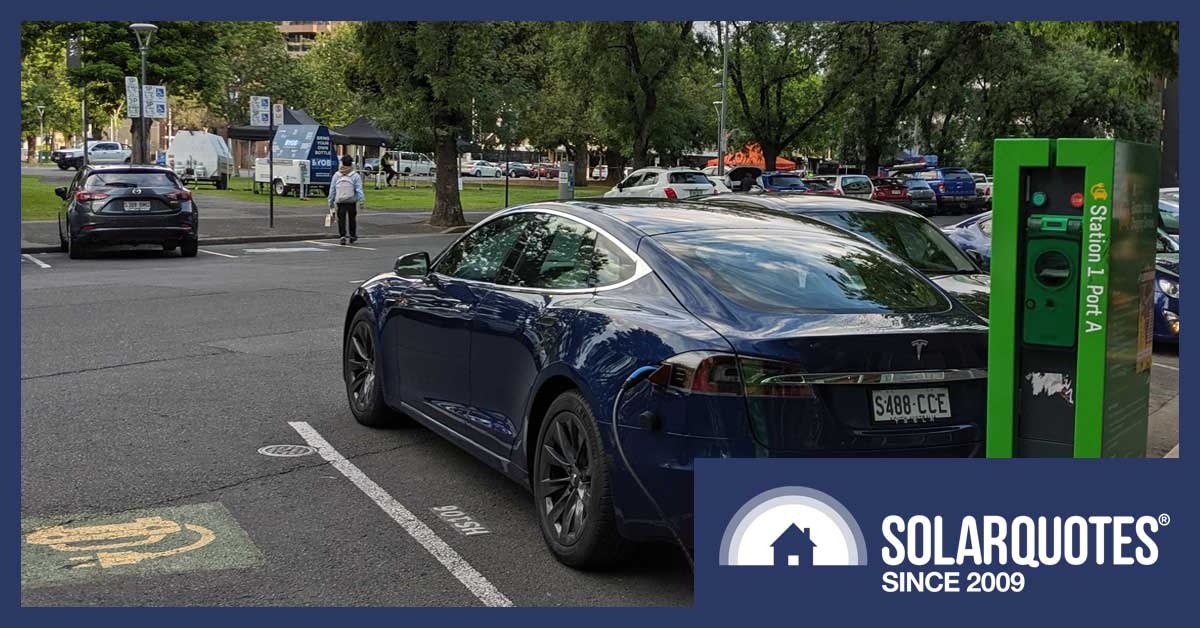

A Chargefox electric vehicle charging station in Adelaide.
If you’re running a still-growing network of 500 EV charging stations across a continent as vast as Australia, you want to avoid low-value maintenance/repair visits to your locations wherever possible.
The Chargefox EV charging network. That’s a lot of distance to cover.
So it’s no surprise automation is on the mind of Chargefox engineer Evan Beaver (@evcricket on Twitter): if an EV charger needs a reset and there’s no fault, why would you want to spend money on a truck roll?
SolarQuotes had the chance to talk to Beaver recently, our interest sparked by a Twitter thread he posted on the topic of automation.
The key to resilience is remote operation, not just of the chargers, but of the electrical system. Chargers have software faults and require resetting sometimes. Electrical gear will trip for electrical faults and other weirdness, often necessitating someone to drive 400km
— Evan Beaver (@evcricket) July 22, 2020
Beaver told me Chargefox needs automation: EV charging stations have to be designed lean.
“They are a minimum viable product. People don’t charge in Gundagai very often! So we want to have as little station as possible, and visit it as infrequently as possible.”
Because the company doesn’t have much redundancy, it needs “incredible” reliability and the ability to fix stuff fast.
Beaver told me his automation project had a simple genesis: an isolation transformer in the Tritium Veefil-PK 350 kW EV chargers Chargefox uses.
He explained that if grid voltage falls, the circuit breakers on those isolation transformers (which also serve a safety purpose, since they disconnect everything if anyone opens the unit’s door) open up.
Chargefox briefly considered adding a UPS to its sites to iron out brief undervoltage events, but that was too expensive.
“You need huge heaters in the cabinet, because if it gets too cold inside, water condenses and the magic smoke comes out.”
Heaters plus UPS ended up too costly, so instead he and other Chargefox engineers decided to see how to operate the breakers remotely.
The answer depends on monitoring, and that comes both from the Tritium chargers and Schweitzer SEL-751 feeder protection relays.
The SEL-751, Beaver told me, has high-accuracy power monitoring and enough built-in smarts to drive relays via PLCs, or electrically driven circuit breakers. For each site, manual operation is the starting point.
“If a breaker trips, we’ll log into our system, and check the voltage feedthrough that period to see whether the grid went on an excursion.”
If voltage fell when the system tripped, he’s pretty confident the breaker can be reset remotely. To protect worker safety, if it tripped because someone opened the unit, the breaker won’t reset until the door is closed again.
More automation came from the capabilities built into the EV charger. If a circuit breaker opens, that can trigger an event – the system takes a snapshot of the grid voltage for a second on either side of the incident, and that trace gets packaged into an e-mail sent to Beaver.
“In step two, if we analyse the [voltage] trace and find it went X-percent out of range, then we can automatically reset it.”
The system is limited to two reset attempts per minute, again for safety reasons. Beaver said Chargefox is close to taking this system from beta to implementation.
Managing Inrush Current
The next challenge Beaver and his engineers had to deal with was the impact of inrush current to the huge transformers when the breaker is closed.
For those unfamiliar with the problem: when you first power up a unit like an EV charger, a lot of power is needed to charge the capacitors and transformers.
The inrush current to a 350kW EV charger is considerable – easily enough to pop a circuit breaker. If that circuit breaker is shared with other circuits (because the charger is hosted at a service station or shopping centre, for example), you can end up with very angry landlords!
“The inrush current is directly proportional to the amount of copper you’ve got [in the transformer]. So if I’ve sized a 700kW transformer, that generates a 10,000 A inrush current.”
So, the aim is to minimise the inrush current. Bever said there are several ways to do this, and some of them sound like science fiction.
The first solution came from Power-tec managing director Dr Michael Jansen. His idea was to use the battery at the EV charger site to balance the inrush current. Bever said:
“When you close the breaker, the battery can sense the inrush current. The battery has energy in its own isolation transformer – so, it closes the switch, and discharges the energy from its isolation transformer into the system, at the same time as the inrush current.”
“That’s a 250KVA battery – it can generate 4MW, for half a second,” he added.
Once the transformer is energised, it turns off.
Precise Timing
That approach only works for EV charging sites that have a battery, so for other sites, other approaches are needed.
One approach is to close the circuit breaker at the moment the AC voltage is crossing zero.
This poses two challenges. The first is that the sites use three-phase power, so the breakers on each phase need to be closed sequentially.
“And you have to close it at exactly the right point, but it takes longer than a phase to get from the meter to the switch. So you have to work out how long it takes for the signal to get there.”
He said his engineer is close to implementing this fix.
“We’ll issue an instruction – we’ll just say ‘please close the breaker’, and the SEL will close the breaker as fast as it can while minimising that inrush current.”
A final option he’s looking at is during the inrush current, a large resistor is switched into the circuit in parallel with the transformer, and as the inrush current falls, the resistor is disconnected.
He’d also like to build a system that can remotely run the mandatory Residual Current Device (RCD) test, as having someone trek the 4,000km covered by Chargefox sites just to test and reset the RCDs is expensive.
Original Source: https://www.solarquotes.com.au/blog/chargefox-ev-charging/

















